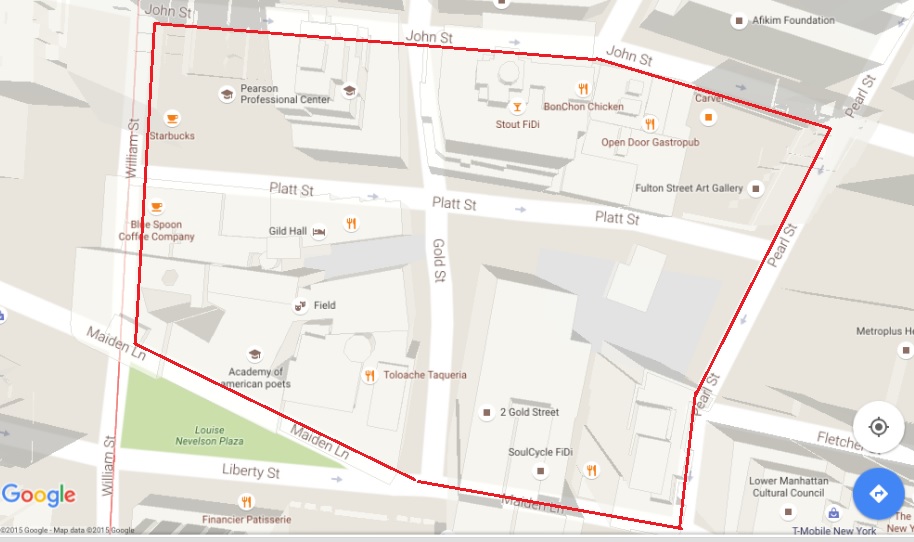
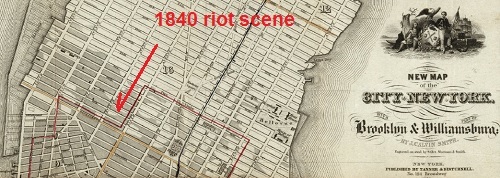
 The map of the city of New York from 1839 shows the extent of development in grey. The streets north of 14th street are newly settled, sitting north of the established municipal wards. They are twice the distance from the tip of lower Manhattan that the rural Lispenard estate and brewery was just fifty years before. The block at 15th street between 6th and 7th avenue is just five blocks below open countryside. Evan’s tweets today on the anti-lager sentiments in the US of the 1850s reminded me of how at that time and in the decades before the setting was not as calm as it appeared. Over a decade earlier, in the Commercial Advertiser of 31 March 1840 reports on an unexpected violent event under the police reports:
The map of the city of New York from 1839 shows the extent of development in grey. The streets north of 14th street are newly settled, sitting north of the established municipal wards. They are twice the distance from the tip of lower Manhattan that the rural Lispenard estate and brewery was just fifty years before. The block at 15th street between 6th and 7th avenue is just five blocks below open countryside. Evan’s tweets today on the anti-lager sentiments in the US of the 1850s reminded me of how at that time and in the decades before the setting was not as calm as it appeared. Over a decade earlier, in the Commercial Advertiser of 31 March 1840 reports on an unexpected violent event under the police reports:
RIOT – On Sunday afternoon a serious riot occurred in 15th street, between the 6th and 7th avenues, which caused great excitement, and was productive of serious injuries to many persons before it was suppressed. It appears that there is a public house in the location above mentioned, kept by a German, where it is common on Sabbath afternoons for persons of both sexes to assemble and indulge in music and dancing, after the manner of the people of the country from whence they come. On Sunday afternoon last, such a party assembled for such purposes, a lady playing on the piano, while others of both sexes were dancing. While thus engaged, a party of young men from the eastern section of the city proceeded to the house in question, and marching into the room where the music and dancing were carrying on, commenced a disturbance by tripping up the heels of the male and female dancers, and throwing them down on the floor. This led to acts of resistance on the part of the party assailed and a fight ensued.
You can read the whole story here but suffice it to say that the scene was nasty. Furniture is destroyed, the parties are beaten, women jump from second story windows. Women get caught up on the fences “caught by their clothes and hung suspended in a most painful and exposed situation” to the jeers of the growing mob. Order begins to be restored when the Mayor himself who rides into the crowd on his horse.
The 1840s is an early point in an ugly era. The Old Brewery at Five Points had been converted into a slum warren three years before. Five Points is said to have had the highest murder rate of any slum in the world. The worst of human experience was lived there. Times were tough. A year before, impeachment proceedings were brought against a grossly profane judge for refusing to take on a role in the management of the police. In October 1839, a riot broke out at the scene of a fire… between two companies of fire fighters. To the north, the first new German immigrants were making a better life for themselves along fresh new avenues neat the city’s rural edge. Tensions did not resolve quickly. The Albany Journal reported a deadly riot at a Philadelphia lager beer tavern in July of 1854. On 10 June 1854, a new political movement of anti-Irish and anti-German nativists or “Know-Nothings” was described in The Weekly Herald of New York, which formed to express antagonism against these newcomers and their ways:
The Germans are chiefly agitated about their lager bier saloons, and are very much incensed at the idea that their liberty to drink as much of that beverage, and at any time and place, as they see fit should be in any danger of restriction.
Change was coming. In 1855, the Evening Post published a very positive report on events at a NYC German outdoor gathering… which included a few well placed rifles. By the late 1850s, the question reached the courts with the ruling of Judge Strong that lager was not intoxicating so therefore could be sold on a Sunday. Times were changing and the children of those Germans attacked in the 1840 riot would become a cornerstone of the nation’s prosperous middle class of the latter end of the century. Along with that, lager does not first succeed because it is a technological marvel. It succeeds because it is a key cultural expression of the new immigrants who would not be beaten down.
*Note, 20 Feb 2016: Gary Gillman emailed right after I posted this and pointed out that this was a couple of years before lager actually arrived. Gillig’s story makes it a bit obscure one way or the other. What did he brew from 1840 to 1846 – and what made the lager he brewed lager?The beer could well have been schenck, a low strength German ale, or even good old local Anglo-American ale. Need to explore this as soon as the New York posts get into the middle third of the 1800s. I am still in the 1790s. So… maybe later this year. Maybe.