The autumn leaves are a ways off falling but the time is coming fast. We have had nothing but great grass growing weather in these parts so more with the mowing than action with the rake so far. And as we say goodbye to saying goodbye, the photo of the week was this one published by Paul Spencer who described the experience:
The autumn leaves are a ways off falling but the time is coming fast. We have had nothing but great grass growing weather in these parts so more with the mowing than action with the rake so far. And as we say goodbye to saying goodbye, the photo of the week was this one published by Paul Spencer who described the experience:
It was surprisingly very good. Big aromas of raisins and port. There was a tiny bit of sourness, but it was much fuller-bodied than I expected. There was quite a lot of sediment and the cork disintegrated upon opening. Would drink again.
As seems to be the trend, not a lot going on in beer writing* this week but let’s see what’s out there hiding. Strategies need to be employed. Hey, this might get things spiced up again:
Maybe I should start a beer fake news website. Does it matter that the brewery in rural Snowdonia set up by two people who gave up their corporate jobs to follow their dream, etc. etc., doesn’t actually exist? How many readers would ever know?
Bring back “Daily Beer Haiku“! That’s what I say… Perhaps relatedly, among all the many confirmations that there is no money in beer writing over the years, this has to be one of the grimmest:
I started to get royalty checks for “The Brewmaster’s Table” in 2015; 12 years after the book was published
Err… as good a warning as any to folk that think there is money in this gig.
Wandering south, it’s odd reading the description of this cidery’s location as the “wilderness” given it’s a farm sitting few miles from Ithaca NY but English folk abroad will be English folk abroad. The piece in Pellicle on Eve’s Cidery in Van Etten in upstate NY is very interesting with some gorgeous photos from the property, highlighting the effect in various areas:
The difference is profound. Though both are superb, recognisably the same variety, boasting voluptuous texture, pristine orchard fruit and seamless acid structure, there is an unmistakable increase in depth and breadth in the Newfield. An upped intensity and unctuousness; where pears and blossom sprung from the North Orchard, here are melons, honeys and the most gorgeous butter popcorn finish. The evidence in favour of Autumn’s conviction is tangible and compelling.
Note: after they slaughtered and pushed out the Indigenous nations and American Loyalists into Canada in the later 1700s** the American Revolutionaries who took the stolen lands found ancient Indigenous apple and peach orchards in northern NY. Perfect place.
Better researched history news. Is that a thing? Liam expanded on his “Hops in Ireland” essay:
…I thought it would be best to do some myth-busting to highlight that hops were grown in this country in various quantities and were even used in commercial brewing. This is a record of the history, mentions and other snippets of information pertaining to hop growing in this country, where I will show and prove that we have been growing hops in this country for the last 400 years at the very least in varying amounts and with various degrees of success, albeit not on the same scale as the bigger hop growing countries.
And Gary continued his series on Imperial brewing in India during the British era, getting into some of the deets including getting into cask tech and the details of brewing at altitude:
As Mumford noted, when the wort boiling in the kettle did not agitate sufficiently, the boiling fermentation might arise. He noted damp firewood might do it, so the boil was less intense than normal, but clearly his high elevation was a major cause. As wort at a mountain brewery would boil below 212 F you would not necessarily get the same agitation as at 212 F., especially with an open boiler. With an enclosed, hence pressurized one, better control could be attained.
Definitely related, Ruvani wrote an excellent personal essay on her experience of the passing of the Queen and how it caused her to reflect on her own life’s arc as a child of Sri Lankans who moved to the UK and the place of beer within it:
English IPA should, by all logic, stick in my throat, yet I continue to devour and praise them. I know full well the excessive damage the British East India Company, purveyors of said IPA did to the Subcontinent, how rich they became from plundering our resources and labor, and how that wealth still circulates among the British elite. How can I, armed with full awareness of the damaging nature of its marketing, enjoy a bottle of Bengal Lancer? And yet not only was it one of the first English IPAs I really rated, I still regard it as an excellent example of the style. Can we separate the beer from its history, its heritage? Can I disconnect my love for it from my own history and heritage?
The passing of the Queen and also the article struck a surprisingly strong chord within me as well. And it led me to an unexpected thought – a middle of the night thought – that more than just a trade, the supply of beer is so often the liquid that actually helps fuel empire’s reach, whether military or by way of commercial hegemony. More than just cash for conviviality. The lubrication to take a nation. Think about it. Just a while ago, I wrote about how Japan’s macro lager was a product of German and American imperialism, shot through with the need to find other uses for the USA’s excess rice production (drawn originally from West Africa long with the stolen people) in the decades after the end of slavery. We see similar things with the German imperial brewing legacy in China and elsewhere. Taunton ale in the 1700s was as much the middle manager’s reward in the sugar production concentration camp plantations of the Caribbean as much as IPA was in India. Beer is not indigenous to North America – it is all colonial. Even this season’s joke of pumpkin beers are an echo of Deleware’s early days as New Sweden in the 1630s. Heck, a Massachusetts’s brewer took Jamaica for England in 1655. It was with the English in Baffin Island in 1577, too. But that all comes after the gunboat commercial diplomacy of the Hanseatic League, those cannon wielding goods traders of the Baltic who pushed hopped beer on northern Europe from the 1200s to the 1400s. You either get them on your beer or just get them when you’re on your beer. If beer is empire, disconnecting may well be a very complex process – even if an entirely worthy one. Peace may be good for beer but oppression may be as well. Maybe beer still helps violent tyranny.
News from the markets of supplies. I hadn’t really been aware of the reason behind the tightening CO2 supply in North America – and it is a bit weird:
Some smaller breweries are even shutting down after a carbon dioxide production shortage caused by natural contamination at the Jackson Dome — a Mississippi reservoir of CO2 from an extinct volcano… The Jackson Dome has provided CO2 to the food and beverage industry since 1977. It became contaminated, cutting off access to a major source of a key ingredient. Experts describe the situation at the site as “dire.”
I suppose non-experts would call it “the shits” or something else less scientific. That being said, switching to the ag update desk, there is some good news from the fields… at least our fields. StatsCan says the Canadian barley crop has rebounded from a dismal 2021:
Higher barley yields compared with 2021 (+59.1% to 68.4 bushels per acre) are projected to more than offset lower anticipated harvested area (-14.8% to 6.3 million acres). As a result, barley production is expected to rise by 35.5% year over year to 9.4 million tonnes in 2022.
That is a nutty per acre yield increase. UK barley sales to the EU have jumped as well but that may be due to drought on the continent. Turkey‘s crop is up 37% and…
The EU-27+UK 2022 barley production is estimated at 59.8 million tonnes, slightly down from the 60 million tonnes seen in May, but up from 59 million tonnes last year.
Hard to keep track of all that. But then… consider the lot of a grain farmer in eastern Ukraine.
The roar of an incoming projectile fills the air, the nearby detonation shaking the ground and sending a plume of black smoke into the sky. Lubinets barely flinches. “I’ve got used to it. It was frightening during the first couple of days, but now — a person can get used to anything,” the 55-year-old said, the smoke dissipating behind him. The farm complex has been hit 15 to 20 times, Lubinets says, and he’s lost count of how many times the fields have been struck. The grain storage has been shelled, the electricity generation facility was destroyed, and multiple rockets rained down on the cattle barn — empty since the livestock was sold off as the war started. Of a prewar workforce of 100 employees, most were evacuated and only about 20 remain.
Wow. Gonna think on that a bit. As we do, please check out the updates from Boak and Bailey mostly every Saturday and perhaps now from Stan usually on a Monday. Check out the weekly Beer Ladies Podcast, and at the mostly weekly OCBG Podcast on a quieter schedule these days – and also sometimes, on a Friday, posts at The Fizz as well (Ed.: we are told ‘tis gone to 404 bloggy podcast heaven… gone to the 404 bloggy podcast farm to play with other puppies.) And the long standing Beervana podcast (Ed.: which I have missed from this list for some unknown reason.) There is a monthly sort of round up at The Glass. (Ed.: that seems to be dead now… nope, there was a post on July 25th… in 2022 even.) There is more from DaftAboutCraft‘s podcast, too. And sign up for Katie’s (Ed.: now very) irregular newsletter, The Gulp, too. And check out the Atlantic Canada Beer Blog‘s weekly roundup. Still gearing up, the recently revived All About Beer has introduced a podcast, too. (Ed.: give it a few weeks to settle in and not be as agreeable… not sure this went very far…) Plus follow the venerable Full Pint podcast. And Fermentation Radio with Emma Inch. The AfroBeerChick podcast as well! And also look at Brewsround and Cabin Fever. And Ben has his own podcast, Beer and Badword (Ed.: …notice of revival of which has been given… still not on the radio dial…) And remember BeerEdge, too, and The Moon Under Water. There was also the Beer O’clock Show but that’s now gone after a ten year run.
*Not even as many B.O.B.s or the usual crop of BW4BW. Some amazingly boring newsletters, too, along with startling blegs for money.
**BTW – proof not to ask good cider makers about history. This is some really well meaning but totally weird colonial denier stuff right in the middle of a self-congratulatory settler ally passage: “So the people fled, the British didn’t give them any food; they starved to death in camps up in Canada. And white people just moved in.” See what really happened was the American Revolutionaries attacked the Haudenosaunee villages (as well as the CNY American Loyalists), destroyed their crops, then forced the survivors west in early winter Nov 1779 to Fort Niagara where there were no supplies and no hope of sufficient resupply – then the Revolutionaries resettled the stolen Haudenosaunee lands. The British actually shared their rations at Fort Niagara. And the British resettled the CNY American Loyalists and Haudenosaunee in what is now Ontario (where I as government official work with their government officials now.) In response, the Haudenosaunee and British burned the valleys in CNY the next fall to establish a buffer zone well south of the lake. Which is even why Rochester NY is not on the lake. That’s why there are communities areas in both Ontario and CNY called the Eastern Gate, Cherry Valley and Schoharie.People ought to know this stuff. I wrote my letter to the editor.
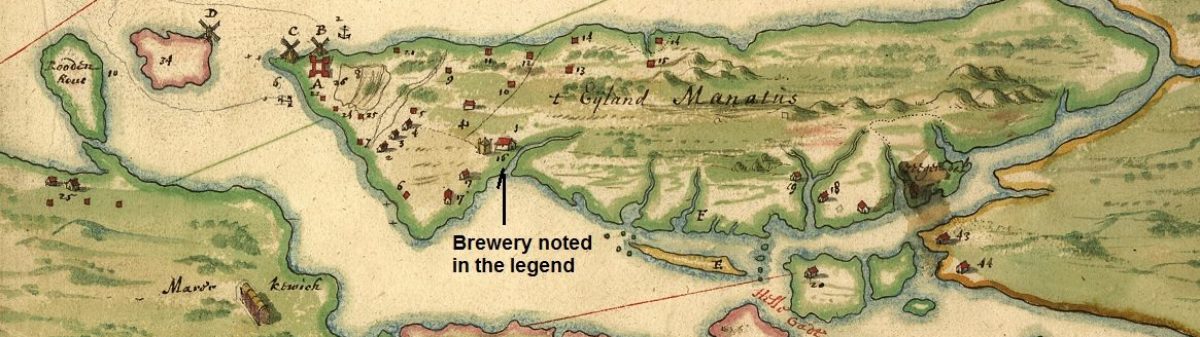




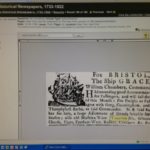
 Next, Hibberts Brown Stout. This stuff is all over the place. Click on that thumbnail. That is a notice from just one store in 1805 stating that they have fifty-five casks on hand with another 498 casks on route. British beer brought in and in bulk. Broadly.
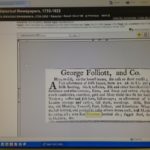
Next, Hibberts Brown Stout. This stuff is all over the place. Click on that thumbnail. That is a notice from just one store in 1805 stating that they have fifty-five casks on hand with another 498 casks on route. British beer brought in and in bulk. Broadly.  Plus, there’s southern beer. You see it in the logs. Click on the ad. Brewing was not practical below a certain latitude so brewers like William Faulkner of NYC and Albany shipped to South Carolina… and the West Indies. He died in 1792. Not to mention there was
Plus, there’s southern beer. You see it in the logs. Click on the ad. Brewing was not practical below a certain latitude so brewers like William Faulkner of NYC and Albany shipped to South Carolina… and the West Indies. He died in 1792. Not to mention there was  And it goes on and on –
And it goes on and on – 

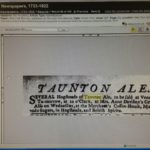
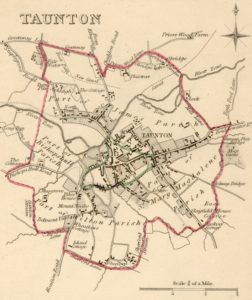 Attentive readers will recall that I have a slow side project in figuring out what I can about Taunton ale. It was a bit of a by-catch to the whole Albany ale thing with references to it showing up in central New York around the time of
Attentive readers will recall that I have a slow side project in figuring out what I can about Taunton ale. It was a bit of a by-catch to the whole Albany ale thing with references to it showing up in central New York around the time of