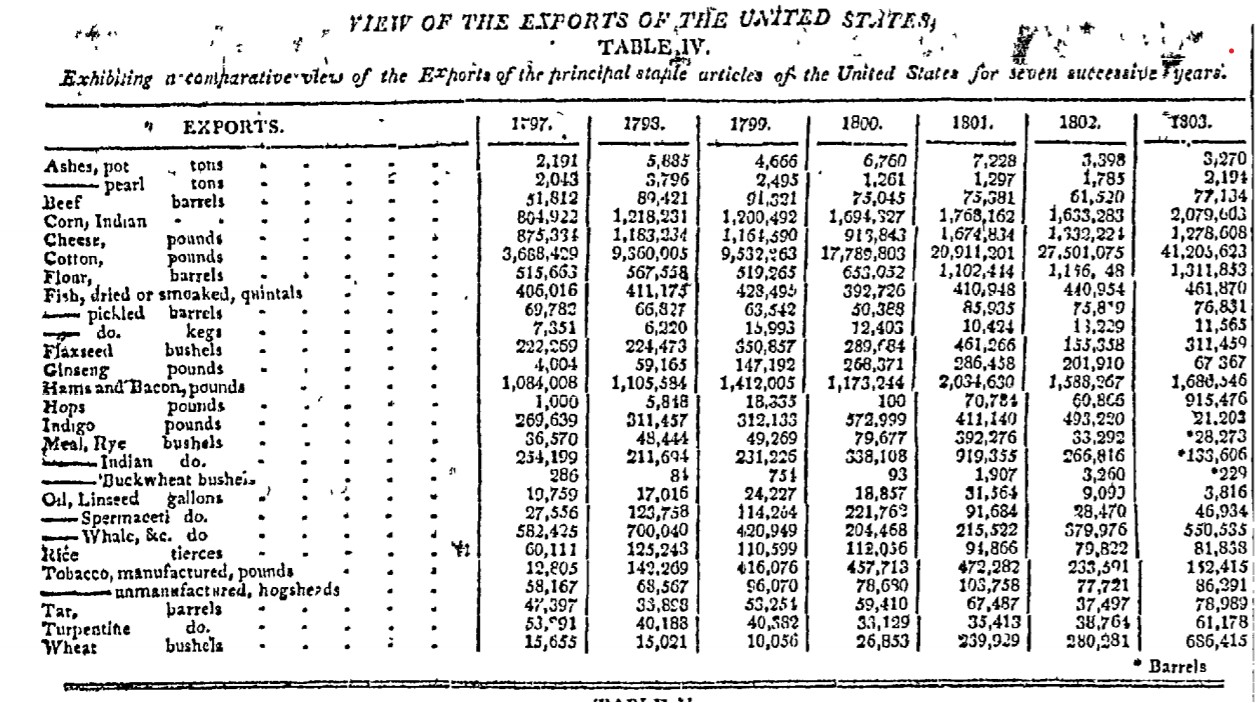
 Above is a table published in The Republican Watch Tower of New York on 4 July 1804. I went looking for this sort of thing after reading Martyn’s excellent post of this week “How Long Have UK Brewers Been Using American Hops? 200 Years, You Say…” Initially, I was interested in the Hesperus, the ship that brought the hops in question to New York to Belfast in 1818. I found notices in the New York newspapers for the same ship bringing Irish linens to the American market on its return voyage. I love ships.
Above is a table published in The Republican Watch Tower of New York on 4 July 1804. I went looking for this sort of thing after reading Martyn’s excellent post of this week “How Long Have UK Brewers Been Using American Hops? 200 Years, You Say…” Initially, I was interested in the Hesperus, the ship that brought the hops in question to New York to Belfast in 1818. I found notices in the New York newspapers for the same ship bringing Irish linens to the American market on its return voyage. I love ships.
 But then I wondered when the first exports of hops from the young United States occurred. And I say “United States” as there is no reason to believe there might not have been colonial exports here and there but I would suggest that is another story. That being said, if the table above is to be believed, hop exports would have begun at least in 1797. But where did they go? One often reprinted 1802 article under the title “To The People of the United States” authored under the name Franklin originally in The Aurora on early US export prospects – the one to the right quoted from The Bee of Hudson, NY – specifically addressed the hop trade and gave a sense of the realities and goes on to conclude:
But then I wondered when the first exports of hops from the young United States occurred. And I say “United States” as there is no reason to believe there might not have been colonial exports here and there but I would suggest that is another story. That being said, if the table above is to be believed, hop exports would have begun at least in 1797. But where did they go? One often reprinted 1802 article under the title “To The People of the United States” authored under the name Franklin originally in The Aurora on early US export prospects – the one to the right quoted from The Bee of Hudson, NY – specifically addressed the hop trade and gave a sense of the realities and goes on to conclude:
The profits of raising hops are such that the great brewing countries of Europe impose heavy duties on their importation from America or elsewhere.
So, soon into the new century US hops were needed at home and subject to European protectionist tariffs. The hop trade to Europe was subject to a prohibition. Which means it had been happening and then was stopped. Which makes one wonder where all those pounds of hops were going, the ones shown in the 1804 table from The Republican Watch Tower. Hmm.
 It is clear that there is a market for hops at the time. The internal inter-state beer trade was certainly robust between New York and New England. Here is a notice that includes 35 sacks of hops on sale in NYC in 1795. In this notice to the right in the New York Gazette of 27 August 1805, 20 bags of hops are on offer. If they are 50 pound bags, that is the same volume of hops listed as the entire export from the nation in 1797. In this edition of Ming’s Price Guide* from New York in August 1810, there are prices for both American and English hops. Still, the international market for commodities like hops has to be understood in the context of tariffs and even international relations during the Napoleonic Wars and at this time we have to be reasonably aware of the Jay Treaty of 1795 opening up trade from the US to Britain and the Embargo Act of 1807 shutting it down again. So if we are looking for an export of hops to Britain from the United States we should keep those dates in mind.
It is clear that there is a market for hops at the time. The internal inter-state beer trade was certainly robust between New York and New England. Here is a notice that includes 35 sacks of hops on sale in NYC in 1795. In this notice to the right in the New York Gazette of 27 August 1805, 20 bags of hops are on offer. If they are 50 pound bags, that is the same volume of hops listed as the entire export from the nation in 1797. In this edition of Ming’s Price Guide* from New York in August 1810, there are prices for both American and English hops. Still, the international market for commodities like hops has to be understood in the context of tariffs and even international relations during the Napoleonic Wars and at this time we have to be reasonably aware of the Jay Treaty of 1795 opening up trade from the US to Britain and the Embargo Act of 1807 shutting it down again. So if we are looking for an export of hops to Britain from the United States we should keep those dates in mind.
 The other thing to remember is that hops are not only native to New York but also grew prodigiously. To the right is a notice for the sale of certain lands in central New York. It was placed in the New York Gazette on 3 May 1805 and notes that “the soil is rich and fertile to produce any species of grain, hemp, etc. – the climate moderate (testified by the abundant growth of vine and hops); the water is good, the salmon and other fisheries great…” So while Craig may be correct in relation to the dates of commercial growing and selling of New York hops, their pre-existing natural abundance was an obvious characteristic of the state. It is also worth noting that when he and I were putting together Upper Hudson Valley Beer, I came across a record from the first decade of the 1700s of Mohawks selling hops to Albany brewer, Evert Wendell.
The other thing to remember is that hops are not only native to New York but also grew prodigiously. To the right is a notice for the sale of certain lands in central New York. It was placed in the New York Gazette on 3 May 1805 and notes that “the soil is rich and fertile to produce any species of grain, hemp, etc. – the climate moderate (testified by the abundant growth of vine and hops); the water is good, the salmon and other fisheries great…” So while Craig may be correct in relation to the dates of commercial growing and selling of New York hops, their pre-existing natural abundance was an obvious characteristic of the state. It is also worth noting that when he and I were putting together Upper Hudson Valley Beer, I came across a record from the first decade of the 1700s of Mohawks selling hops to Albany brewer, Evert Wendell.
And hops were not just picked wild at the time. In
The New and Complete American Encyclopedia, 1808 edition, there is an extensive section on the propagation and selling of hops including information taken, it is cited from a document published by the Agricultural Society of New York… no, the Society for the Promotion of Agriculture, Arts and Manufactures, instituted in the State of New York.** The cultivation in New York is especially encouraged:
The cultivators of land in this state have every inducement which policy or inducement can afford, to enter, in spirit, into the cultivation of hops. We shall therefore be enabled to supply our own demand, and export this article; instead of sending abroad for all we use; and no crop that can possibly be put on land will yield an equal profit…
Were the hops loaded on the Herperus in 1818 destined for a Belfast brewery the first hops sold into the British market? It’s quite unlikely given the abundance of native hops, the records of an export trade, public marketplace pricing and the general regular European trade in many commodities going back a couple of centuries. Was there a Caribbean market for hops along with the wheat and biscuit shipments we see bound to supply an aspect of the slave trade? Could be but southern brewing of beer was a very dodgy thing.
It’s also likely that it was a little remarked upon activity, like the export of casks of beer from Albany and New York City. Likely modest supplies of infilled cargo rounding out a vessel’s hold. As usual, we are at the whim of the vendor from the time – was there enough demand to spend the money to place the notice in the newspaper? Without someone making that decision then it is difficult to know now what they were particularly up to. But such is life, the record of the activity never being proof of the fact of the activity.
Still, there is likely more to be found out there – especially in relation to activities such as Strictland’s study in the years after the end of the Revolution when interest in trade between the newly independent nation and the home of its often Loyalist heart in the old country seemed to tick up before the laws came down. So let’s consider this an introduction to the idea.
*aka Dickinson’s (Formerly) Ming’s New-York Price-Current, Ming and Young’s New-York Price-Current, Ming’s New-York Price-Current, Oram’s New-York Price-Current, Oram’s New-York Price-Current, and Marine Register, The New-York Prices Current.
**The NY Agricultural Society as it exists today only comes into being in 1832… which seems a bit late given the county ag fairs start up years earlier.