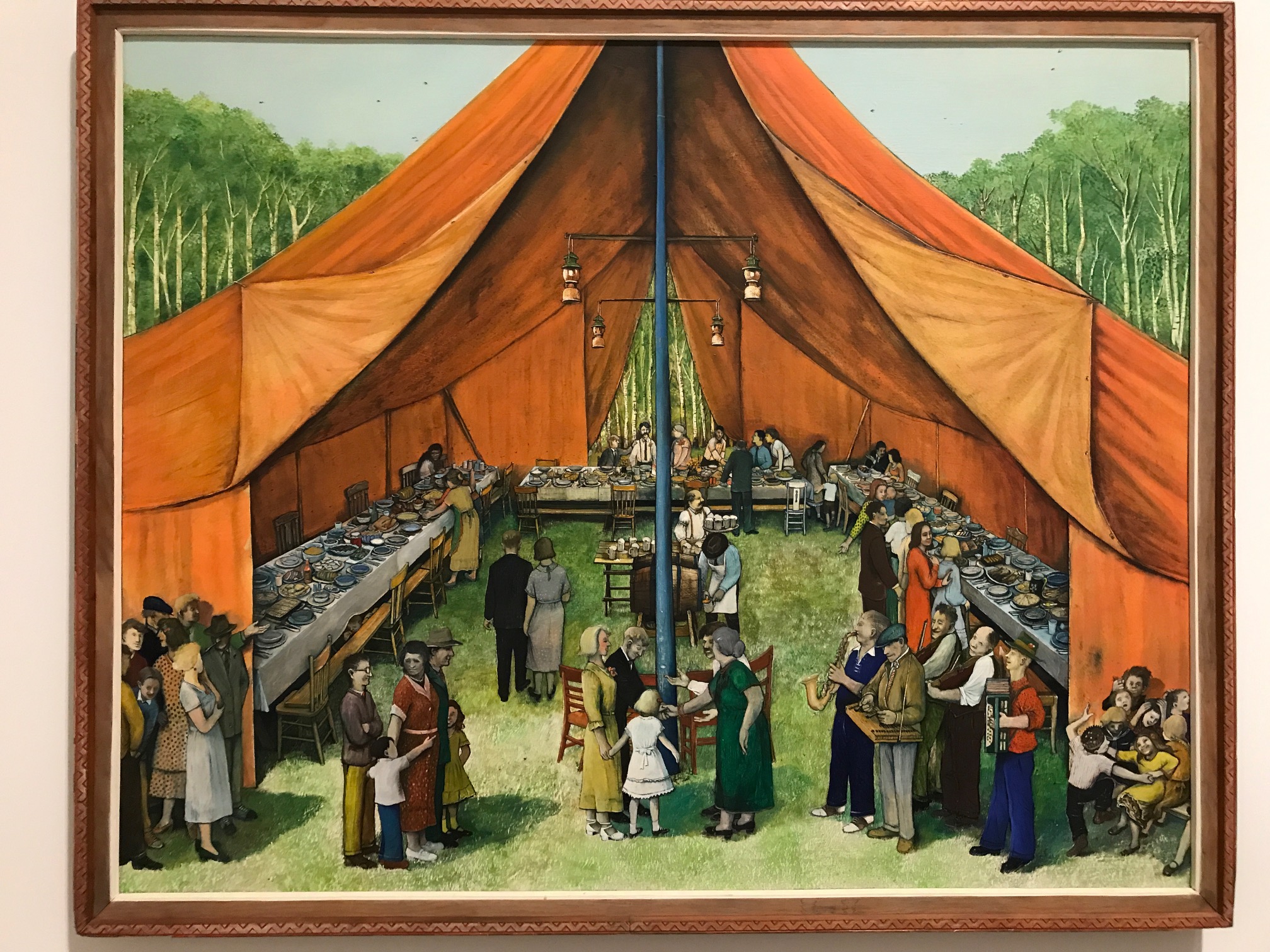
This week’s big news saw me and mine on the road. I was up in the nation’s capital over Saturday and Sunday and took part in my kind of beer tourism. By that I mean actually doing normal things while noting beer around me and having one when the more important things in life were not imposed upon. We took in an hour at the National Gallery of Canada and spent time in the Canadian exhibits, where I came across this painting, Manitoba Party, from 1964. Cheery and folk artsy, right away I noticed the kegs and beer distribution smack dab in the middle. More detail below.
This week’s big news saw me and mine on the road. I was up in the nation’s capital over Saturday and Sunday and took part in my kind of beer tourism. By that I mean actually doing normal things while noting beer around me and having one when the more important things in life were not imposed upon. We took in an hour at the National Gallery of Canada and spent time in the Canadian exhibits, where I came across this painting, Manitoba Party, from 1964. Cheery and folk artsy, right away I noticed the kegs and beer distribution smack dab in the middle. More detail below.
Speaking of Canada, Frank Zappa once said that you can’t be a real country unless you have a beer and an airline. Canada obsesses about such things, often when there is little in the news other than, you know, affirmations. Mr. B has picked up the theme:
I’ve no idea what Canada’s national beer style might ultimately be, whether it will be hop-focused or yeast-based or feature some ingredient that it true to the Canadian spirit.
Not sure that is a big worry of mine. Zappa went on to that that it also “helps if you have some kind of a football team, or some nuclear weapons, but at the very least you need a beer.” We have our own form of football. And, really, the good neighbour has enough of those bombs. Art, however. That works for me.
Looking back on the rest of my week, I find I have to take something back* from last week’s news notes. I wrote that we would have to spend a “happy early December without an edition of #TheSession” but Stan is giving us one last kick at the can with the topic “One More For The Road” in which we are asked to:
Pick a beer for the end of a life, an end of a meal, an end of a day, an end of a relationship. So happy or sad, or something between. Write about the beer. Write about the aroma, the flavor, and write about what you feel when it is gone.
Not particularly Yule-drenched but there will be a few weeks afterwards to get oneself back in the spirit. With any luck, the responses will give J. Wilson some cheer, given his tweet this week which is about as broadly grim as one might get:
Sometimes I worry about the future of beer since so many beer lovers today don’t even like the taste of beer.
Me, I am more hopeful than that – especially given how beer and brewing has survived any number of false gods and dead ends over the centuries. December is actually an excellent time to get back in touch with the classics and leave the NEIPAs and other alcopops to the amateur drinkers. Alistair of Fuggled fame has offered us one route to set things back in their proper order:
…it seems that Craft Beer™ Advent Calendars have been all the rage in recent years and I thought I’d jump on the old bandwagon. Only one minor issue, I have an aversion to having stuff curated for me, I much prefer to survey what’s available and make my own decisions, yes I can be something of a contrarian, I know. The plan as it currently stands is to buy 24 bottles of seasonal beers, drink one each day of Advent, and then write a blog post about it…
Wonderful. A blog plan. Nate has also offered us a route forward for his beer blogging for 2019 and beyond:
…I gave up on the Beats element about music years ago as I stopped listening to so much music, and frankly, my music reviews weren’t very good at all. So, I needed to replace Beats with something and given my love for professional wrestling, why not change it to Beatdowns and write about wrestling since I watch so much of it? So, from now on, this blog will be known as Booze, Beatdowns and Bites.
There was a university radio show near me that I liked a decade ago named something like “Hardcore Grooves and Wrestlin’ Moves” so this should work for me.
Here’s an interesting twist on the recreation of one historic brand of beer – the rights to brew Syracuse NY’s Congress beer were acquired by the local historical society!
In more real news, BarMas that objectified human point of fascination of mine – for his superhuman chore doing and vernacular booze production skills – has posted about his new orchard:
Originally, the ends of every row had cherry trees, which our current plot is missing, so we will gain, I think, 5 very large cherry trees. Inside the cherry trees, each row then had a few pear trees, and this is repeated a thee ends of the rows we are purchasing. Mostly they seem to be conference, mirroring the ends of the current rows, but there are a few other varieties, like Bürgermeisterbirne/Köstliche aus Charneux, and I hope some perry pear trees and more Williams Christ.
Wow. Riddled. Jealousy.
The serious news in the business of beer as it affects Canada and beyond has been reported upon by my pal Josh Rubin in the Toronto Star:
DME, a P.E.I.-based equipment manufacturer with facilities in B.C. and South Carolina, was in receivership, with more than $18 million owed to RBC and an unspecified amount to other creditors, including the company’s own 250 employees. The company’s directors have all resigned, and a B.C.-based receiver has been appointed to explore either a liquidation or sale of the company, with offers due by Jan. 7.
Big news. And a bit strange news. First, though, gotta tell you. I know folk involved, the lawyer bringing the receivership and even the judge granting it,** and have no doubt as to the realities but the effect is going to be widespread. Josh*** got Jason Fisher**** on the record to explore what losing a $800,000 deposit means to him and his brewery. What gets me is that the required cash injection was allegedly only $5,000,000 which seems like a paltry sum in the face of 250 jobs – that’s just $20,000 a job – and especially given the work they were getting including being a supplier to the new Guinness brewery in Baltimore. Where is the ACOA money? Where was Wade… who I also know… former law school prof. Also, before you buy brewing equipment, here is some reasonable advice on securing your deposit.
There. By next week will be another one gone and one closer to Yule. I am more of a Dec 15th to Jan 10th sorta holiday season person. Other versions exist. Many are US Thanksgiving to Dec 25th holiday-ers, immediately stripping the house of tree and tinsel thereafter and, presumably, getting a bit drunk on New Years Eve then staring out the window waiting for spring. Not me. I want to realize that the sun has made at least three weeks worth of its way back to equinox before I come around to reality. Then, I want be out in the winter woodland to hear the chickadees calling out for mates and, well, we all know about chickadees, right?
I am sure there still will be beer news throughout. Just like Boak and Bailey know and report out on each Saturday. Feel nostalgic? Go check out some Xmas contest entries from Yuletides past. Link to the right…
* No, not what caused this weird blurt… which looked like a 1.3 violation with perhaps a 1.2 twist.
** I practiced law in PEI from 1998 to 2003. Respectively (i) co-associate pal and (ii) respected partner of another firm and colleague of my counterpart respectively.
*** Who I know in the fellow beer writer sense.
*** Who I don’t know but think I had a brief flame war with once.