Erg. I have post Victoria Day general body disorder. When one is a young adult in Canada, the May 2-4 weekend can lead to the three day hangover version of VDGBD but in my case it is merely a case of too much gardening. Joining the overwintered leek, kale, parsley, parsnip, garlic and green onion are new seedlings of red lettuce, beets, basil, romaine and radish. Hoeing and mulching and mowing and digging sessions along with timid pruning of the Pinot Noir filled the weekend after which a few well placed Sam Roberts Band ales from my local Spearhead brewery store hit the spot. I have no comment on the concept of the collaboration as that only affects what is outside the can as opposed to inside but as a nice brown ale at 4.5% it did the trick.
Gardening was on my mind in another way this week. If you don’t read the wine writer Jancis Robinson you are missing something. I say wine writer but for my money she is the best drinks writer working today. Consider this column she wrote on “premox” or premature oxidation as currently found in premium white Burgundies. There is a massive raft of information embedded in the writing including very firm opinion – “One wine, a Boyer-Martinot Meursault Charmes, was as dead as a dodo…” to details on how global warming might affect the value proposition as to grape growing acreage in the Burgundian geography. Fabulous. When I tell Stan that wine making, for me, is at least as complex as brewing, this (along with working my own current second vinyard-ette) is what I mean.
Book news. Jeff says Barrel Aged Stout and Selling Out, the new history of Goose Island by Josh Noel, is a something of revelation, framing important things for we who are sitting as we are now here in this one year seemingly just minutes after the era of the great craft buy-outs:
Throughout the book, people on both sides think there’s a way to square this circle, to bring the best of craft and big beer together. The second half of BASSO lays bare why that was never possible. The good and bad of each approach are actually just the positive and negative qualities of the same thing. It’s just not possible to be both revolutionary and cautious. As the story plays out, these cultures clash, and one comes out triumphant.
Sounds pretty fabulous. Go buy the book.
Blogs are back! As with Jordan two weeks ago, ATJ renews his pledge to his blog and post a tale. Blogging is totally back, baby. Jordan has even doubled his output with this tale of salty nuts. Totally. Back.
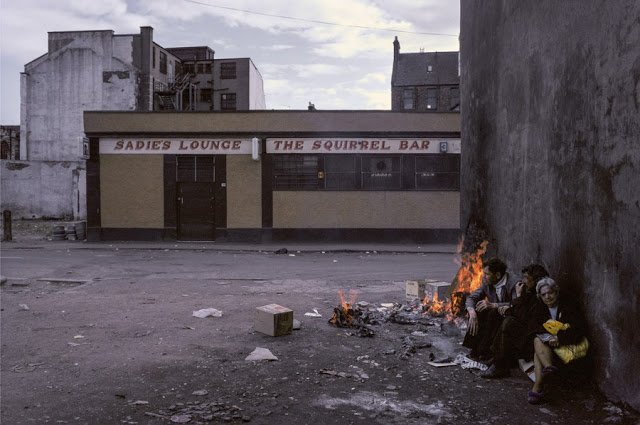
From the twitter feed “Picture this Scotland” comes this view of Glasgow in 1980:
Better than a Bill Forsyth film, that up there. Memories flood in. I remember my father when I was seven giving us a tour of the areas of Glasgow which were still bombed out from the war. Up there with the time when I was fourteen he took us to the square in his hometown of Greenock at noon on a Tuesday to watch the drunk men eat mittfuls of chips while simultaneously falling down. Did I mention Dad was a minister of the cloth? Note: The Squirrel has some history and seems to still be… active.
Well… except for there being no beer in California in 1927 and there being plenty of US dark lager both before and after prohibition…
The Chicago Tribune published an excellent article in the form of real beer business journalism on the fall and possible rise of Constellation’s billion dollar bauble, Ballast Point, a beer brand for me which always screamed “price too high!” for the quality one received. Apparently others agreed:
Michigan-based Founders Brewing Co., best known for its lower-priced, lower-alcohol All Day IPA, was roughly the same size as Ballast Point in 2015, but could end up shipping twice as much beer to wholesalers this year. Founders CEO Mike Stevens called the Ballast Point decline a “perfect storm” of high price point — a six-pack of Sculpin regularly sold for $15 — and what he believes to be a fading trend in fruit-flavored IPAs. “They were obviously just screaming to the top of the peak, riding that price point, riding their fruit IPAs. … Right when that (deal) went down, we kind of all knew that they were going to have to fix the price points because the consumers were going to lose interest,” Stevens said.
Mmm… fruit beer. Expensive fruit beer… Not sure I need a resurrection of that anytime soon. What’s next? Andy is lobbying for a gimmick free summer. That would be nice.
Conversely, news out of central New York… err… the Capital Region… finds the clock actually being turned backwards as a bricks and mortar brewery, Shmaltz reverts* to being a contract brewer – just as they had been prior to 2013. I was a regular buyer of their beer a decade or more ago so it’s certainly a brewer whose brands never suffered from someone else owning the steel. Happy story likely in the making. Maybe?
Ales Through the Ages II looks fabulous. Might I get there?
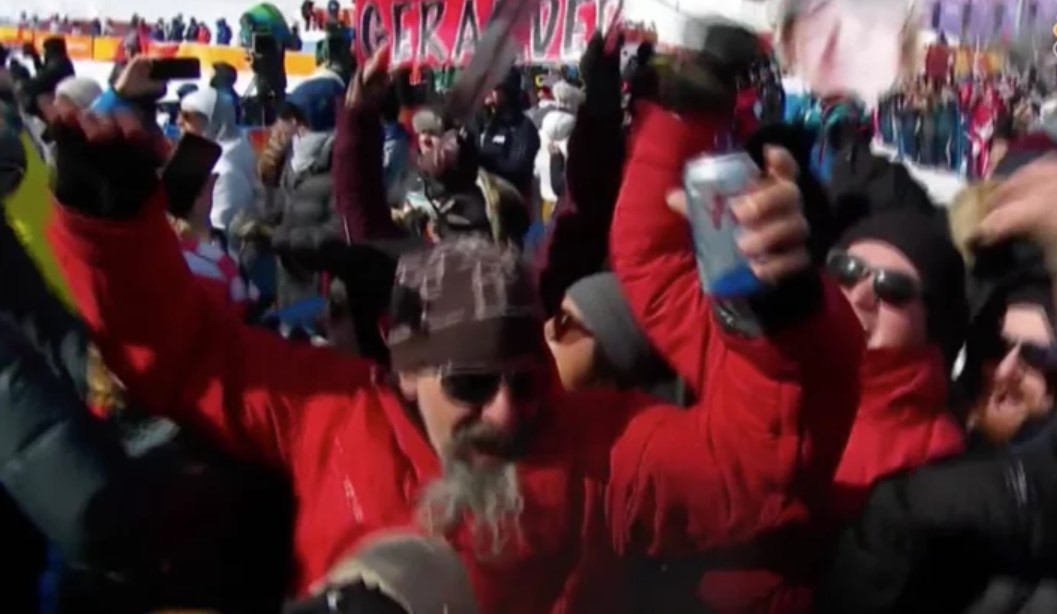
 Ontario election time beer update! Suddenly serious contenders to lead the next government, the New Democratic Party, might review the rather slim introduction of beer, cider and wine into a handful of grocery stores across the province. Current Premier and solidly slipping third-place candidate Kathleen Wynne says expanding beer to more privates stores is just… just… well, “it’s not sensible”! And Doug “Did I Just Peak Early?” Ford says – beer sales everywhere! That ain’t happening but at least, as shown above, he wins the prize for the first beer pour at an election stop, part of Canada’s great “politician pouring beer” heritage. Note: someone’s angry. Note2: Ben says none of this matters. Two weeks to election day. Stay tuned.
Ontario election time beer update! Suddenly serious contenders to lead the next government, the New Democratic Party, might review the rather slim introduction of beer, cider and wine into a handful of grocery stores across the province. Current Premier and solidly slipping third-place candidate Kathleen Wynne says expanding beer to more privates stores is just… just… well, “it’s not sensible”! And Doug “Did I Just Peak Early?” Ford says – beer sales everywhere! That ain’t happening but at least, as shown above, he wins the prize for the first beer pour at an election stop, part of Canada’s great “politician pouring beer” heritage. Note: someone’s angry. Note2: Ben says none of this matters. Two weeks to election day. Stay tuned.
Well, look at that. That was largely a fairly positive week, wasn’t it! No inter-consulto insult fests. No big craft hyperbolic pontifications. Am I growing up or something? That would be weird. Don’t forget that the beer news never sleeps and check out Boak and Bailey on Saturday. Stan is on holiday somewhere south of the equator… again. “Good Old South of the Equator” Stan. That’s what they call him. He’s posting from there. But not on Mondays in June. No, sirree. Not “Good Old South of the Equator” Stan.
*As reported by Deanna Fox, someone I have actually met.