From Sessional Papers, House of Lords, 1840
—-
The following was recorded in evidence at the Old Bailey on 9th December 1778 in a case of grand larceny.
Mr. PETER CORBETT sworn.
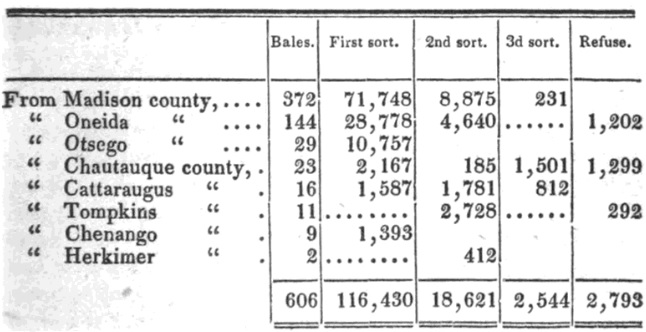
I am Bengal warehouse-keeper to the East-India Company. I have in my hand the invoice of the Duke of Portland; this was delivered to me from the company when the ship arrived, and it is my duty to see that every thing comes out clear from these packages into the warehouse agreeable to the invoice sent from the company’s servants at Bengal . In the second page, here is a No. 4. S. Taffety, which means striped taffety. Upon the opening of this chest, the servants under me gave me what we call a piling bill; they found only 176 pieces and a small bale containing ten, and this piece, which was kept for evidence. These goods were in a strong chest, nailed down, and there was a strong gunny or hopsack sewed upon it.
Hopsack. I know a bit about hopsack now as I own a blue blazer made of the stuff as well as a pair of black trousers. Neither Mr. Corbett in 1778 nor Mr. Lidbetter likely did. For them hopsack was definitely a packing or wrapping material. It’s formed by making your cloth in a basket weave. Often wool for clothes. Hemp and jute for bagging. Made into a jacket, it’s light summer weight cloth, the open weave letting the air flow. Fine fashion by the 1890s. For sacks and bags it’s strong, perhaps a grade or two above burlap.
The House of Lords was inquiring into the general economic circumstances when it was considering hopsack during its 1840 session, J. Mitchell, Esq., LL.D., Assistant Commissioner of the Hand-Loom Inquiry Commission reporting from the east of England. They learned about sacking and floor-cloth weaving in Reading, Berkshire and specifically Mr. William Harris of the delightful address, the “Hit or Miss beer-shop in Boarded-lane” who described the sad local state of affairs:
In the year 1815 there were as many as 11 masters and about 200 looms; now there are not 12 looms. The trade began to fall off in 1821, and has gradually become less and less, and when the old men, the present weavers, are gone, it is supposed this trade will be at an end in Reading. No person has learned the trade for years past. The price paid for weaving in 1815 was 2 J d. the square yard; this was reduced to 2 4 d., and afterwards to 2 d. per square yard. The sacking is three-quarters wide, or a little more. There is a great deal of time lost for want of regular employment.
There is now only one loom at work making floor-cloth. The web is six yards broad. There are looms which make floor-cloth eight yards wide, and even 10 yards wide. The cause of the want of employment in this branch is inability to manufacture the goods, and come into the market at the same price as the manufacturers of Dundee. The local advantages of that town in obtaining the raw material, in spinning and weaving and sending the goods to market, are such as to leave no chance for competition. The remnant of the business still lingering in Reading is the supply of the neighbouring farmers with sacks. There is no remedy, and with the present race of weavers the trade becomes extinct.
As stuff in demand, locally made Reading coarse packing cloth was on the way out. Why? Trains. It’s always the trains. Or the canals before them bringing in that cheap Dundee sacking… or a cheaper or tastier strong ale. Secondary manufacturers making the packing for the primary producers don’t need to be local when the trains can bring in stuff that’s as good for less. Mr. Lidbetter up there up top? He seemed to still be bucking the trend. He had a market the lads of Dundee couldn’t crack:
There is one article in which there is a decided advantage, that is hop bagging. The town is the very centre of a rich hop district. The consumer, therefore, is close at hand. The hop bagging is made very substantial. As it is the custom when the hops are sold to pay by the pound of the gross weight, hops and bag together, the hop grower has no interest in using a slight fabric.
See the trick? Heavy sacking for the hops, higher price for the sack of hops. You don’t get that advantage by the train load.







 The title of the patent from 1832 is titillating: “US Patent: 6,894X – Restoring sour or musty beer or ale to its original purity by rebrewing.” Sadly the
The title of the patent from 1832 is titillating: “US Patent: 6,894X – Restoring sour or musty beer or ale to its original purity by rebrewing.” Sadly the 
 Gary
Gary